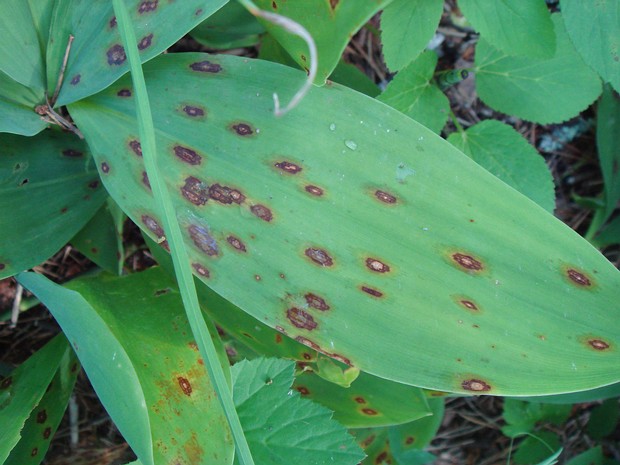
Botrytis convallariae - Ботритис конваллиарийский - Lily blight - Maiglöckchen-Blattfleckenpilz
Botrytis convallariae is a species of fungus in the family Sclerotiniaceae, within the order Helotiales of the Ascomycota phylum. It is commonly known as lily…
11 images
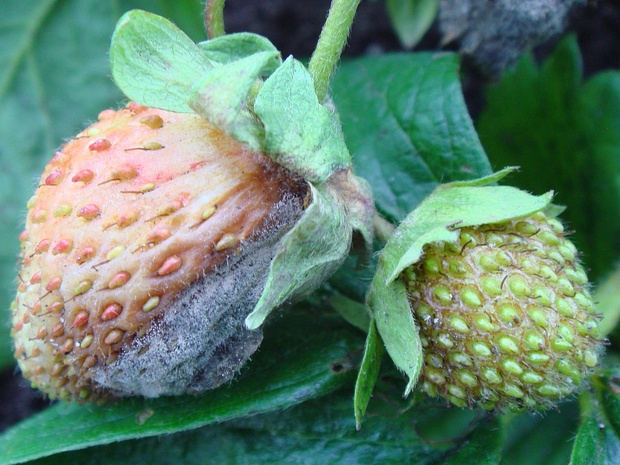

Botrytis cinerea - Ботритис серый - Gray mold - Grauschimmel
Botrytis cinerea is a species of fungus in the family Sclerotiniaceae, within the order Helotiales of the Ascomycota phylum. It is commonly known as gray mold…
5 images
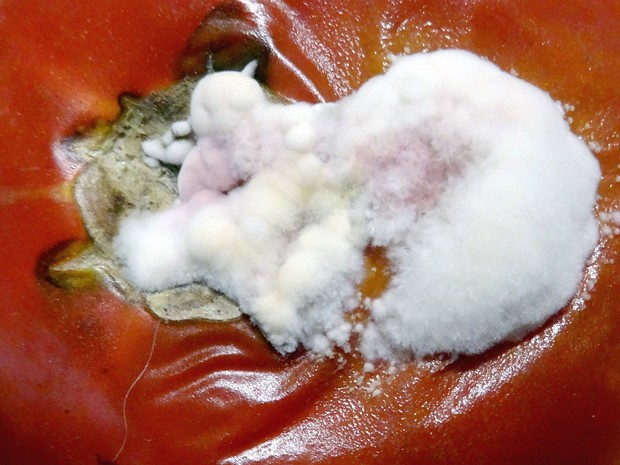
Sclerotinia sclerotiorum - Склеротиния кочанная гниль - White mold - Weißer Schimmel
Sclerotinia sclerotiorum is a species of fungus in the family Sclerotiniaceae, within the order Helotiales of the Ascomycota phylum. It is commonly known as…
11 images
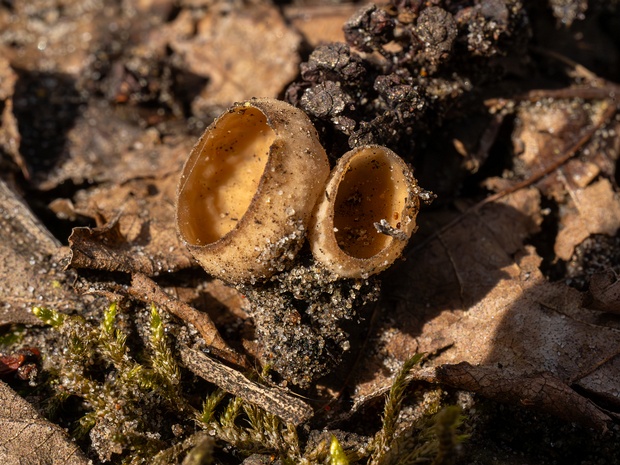

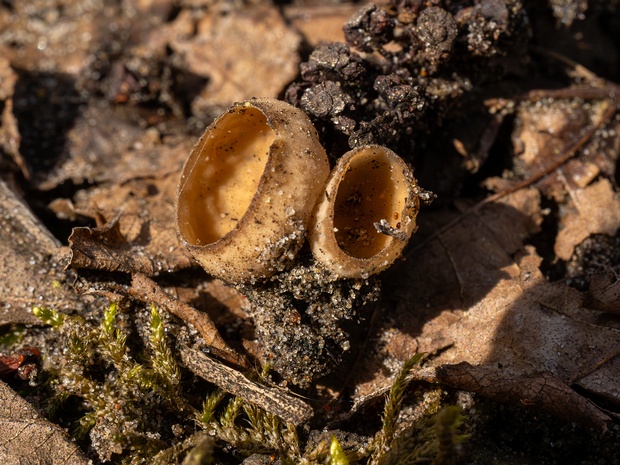
Ciboria amentacea - Цибория желудевидная - Alder Ciboria - Haselbecherchen
Ciboria amentacea, a unique species of fungi, belongs to the family Sclerotiniaceae within the Ascomycota phylum. These fungi are commonly found in Europe and…
139 images
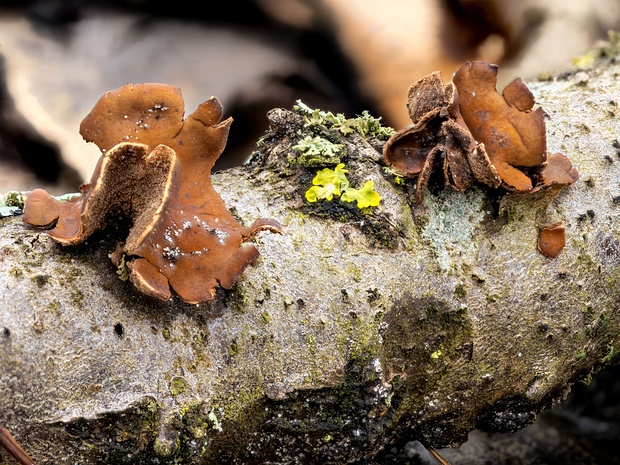

Encoelia furfuracea - Энцелия шелушистая - Spring Hazelcup - Hasel-Kleiebecherling
Encoelia furfuracea is a species of fungus known for its distinctive appearance and ecological role. It typically has small fruiting bodies with caps ranging…
25 images

